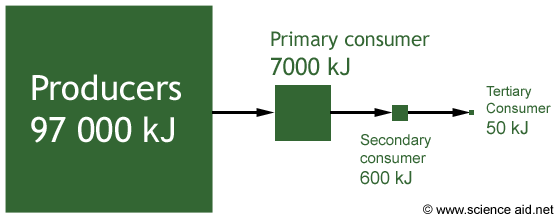
The reason why not all of the energy will make it to the next tropic level is that some of it will be used up on the level it is at. The energy is used for the life processes of the animal that it is in.
e.g If a bunny rabbit eats a cabbage, it will use some of the energy to keep warm, some to move e.c.t so fox only gets some of the original energy from the cabbage.
This blog will cover and explain the specification for Edexcel triple science course 2013 for biology. Hope it helps :)
Showing posts with label Feeding relationships. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Feeding relationships. Show all posts
Saturday, 30 March 2013
4.6 understand the transfer of substances and of energy along a food chain
As one thing consumes another the energy and other things inside it- for example fat and vitamins- get transferred to the consumer. If you eat a fatty piece of beef you get the fat from the cow.
4.5 understand the concepts of food chains, food webs, pyramids of number, pyramids of biomass and pyramids of energy transfer
 |
| sciencebitz.com |
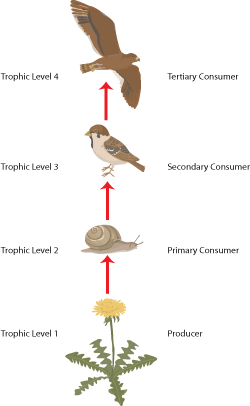
A food chain shows the transfer of energy up the food chain beginning with the producers then the primary consumers and so forth.
| king.portlandsschool.org |
A food web links several animals within a habitat showing what consumes what and is consumed by what.
 |
| BBC.co.uk |
 |
| BBC.co.uk |
 |
| scienceaid.net |
Saturday, 23 February 2013
4.4 explain the names given to different trophic levels to include producers, primary, secondary and tertiary consumers and decomposers
Different trophic levels= different feeding levels
Producer (turns light energy into chemical energy)
v
Primary consumer (eats the producer and gains its energy)
v
Secondary consumers
v
Tertiary consumers
When these organism die they are broken down by decomposers- fungi and bacteria.
Producer (turns light energy into chemical energy)
v
Primary consumer (eats the producer and gains its energy)
v
Secondary consumers
v
Tertiary consumers
When these organism die they are broken down by decomposers- fungi and bacteria.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)