Sewage contains nutrient which enable algae to flourish. They take up sunlight and oxygen. Many fish die and other organisms die. Decomposers thrive on there dead bodies; meaning even more oxygen is taken up by microorganisms.
Basically its the same process as eutrophication.
This blog will cover and explain the specification for Edexcel triple science course 2013 for biology. Hope it helps :)
Showing posts with label Section 4. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Section 4. Show all posts
Friday, 17 May 2013
Sunday, 21 April 2013
4.17 understand the effects of deforestation, including leaching, soil erosion, disturbance of the water cycle and of the balance in atmospheric oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Leeching is basically loss of nutrient from soil. Normally nutrient is rained into the soil; absorbed by plants; shed in their leaves/when they die; digested by decomposers so its back in the soil. If you take away the vegetation you remove nutrients from the cycle. In addition to this the soil is not protected by plants and so when it rains there will be a higher rate of surface run off, this will take the nutrients from the soil with it. Soil erosion is also caused by the fact that without plants to protect the soil there is more surface run off, because soil is taken with it.
Plants absorb water from the soil and lose water from their leaves (through transpiration) in to the atmosphere which goes on to make clouds. If there are less plants then less water is evaporated into the atmosphere, this means there are less clouds; less clouds means less rain, which can mean drought.
Plants also convert carbon dioxide into oxygen when they photosynthesise. Forests carbon sinks, they use more carbon than they release: this means they help to make sure there aren't too high levels of CO2 in the atmosphere. When forests are cut down this process is lost and additionally the trees are usually burnt which releases CO2 into the atmosphere.
This article is explains some of the effects of deforestation nicely:
http://rainforests.mongabay.com/0902.htm
Plants absorb water from the soil and lose water from their leaves (through transpiration) in to the atmosphere which goes on to make clouds. If there are less plants then less water is evaporated into the atmosphere, this means there are less clouds; less clouds means less rain, which can mean drought.
Plants also convert carbon dioxide into oxygen when they photosynthesise. Forests carbon sinks, they use more carbon than they release: this means they help to make sure there aren't too high levels of CO2 in the atmosphere. When forests are cut down this process is lost and additionally the trees are usually burnt which releases CO2 into the atmosphere.
This article is explains some of the effects of deforestation nicely:
http://rainforests.mongabay.com/0902.htm
4.16 understand that eutrophication can result from leached minerals from fertiliser
Eutrophication is when there are excessive amounts of nutrients in a lake. The effects of this are that algae will bloom (grow quickly). Having a lot of algae will mean that there is not enough oxygen for other organisms, they will also struggle to find enough light as algae covers the surface. More organisms will die then usual- more algae to die/ less oxygen and light so fish die- so decomposers will thrive; these decomposers will also use a lot of oxygen from the water. In the end there will not be enough oxygen for fish.
Nutrient get leached into rivers from soil as rain water runs off land into rivers and lakes taking nutrient with it. If fertiliser has been put in the soil then the soil will be rich in certain nutrient, especially nitrogen: so rain water runs off fertilised soil it will bring high amounts of nutrient into surrounding rivers or lakes causing eutrophication.
Nutrient get leached into rivers from soil as rain water runs off land into rivers and lakes taking nutrient with it. If fertiliser has been put in the soil then the soil will be rich in certain nutrient, especially nitrogen: so rain water runs off fertilised soil it will bring high amounts of nutrient into surrounding rivers or lakes causing eutrophication.
4.14 understand how an increase in greenhouse gases results in an enhanced greenhouse effect and that this may lead to global warming and its consequences
The sun heats up the earth with infra-red waves that it emits, these waves travel from the sun through the earth atmosphere and warm it up. The earth emits its own rays so that it maintains its heat instead of just warming up forever! Many of these rays escape the earth's atmosphere- revealing it of heat- but some are absorbed by certain gasses- Greenhouse gasses- this means the heat is trapped within the earth's atmosphere. On a large scale this heats the earth, which we call global warming, and this can lead to climate change: the expected weather patterns reverse or exaggerate: this is thought to result in natural disaster (drought, floods).
4.13 understand how human activities contribute to greenhouse gases
Many of the processes that we carry out in homes and factories produce or release gasses with the greenhouse effect. Many things release greenhouse gasses when they are burned; reactions can create greenhouse gasses; some plants and animals that we keep a lot of naturally release greenhouse gasses. Processes that produce greenhouse gasses include burning fossil fuels and keeping large amounts of live stock.
4.12 understand that water vapour, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, methane and CFCs are greenhouse gases
A green house gas is one that absorbs heat reflected by the earth, this heat is then trapped in the earth's atmosphere warming the earth. In large quantities these gasses can change the climate by keeping in too much heat. Gasses that do this include: water vapour, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, methane and CFCs.
A CFC is a compound that contains only carbon, chlorine, hydrogen and fluorine.
A CFC is a compound that contains only carbon, chlorine, hydrogen and fluorine.
4.11 understand the biological consequences of pollution of air by sulfur dioxide and by carbon monoxide
Sulfur dioxide and carbon monoxide are created by many processes we use in factories and homes. When in the atmosphere they can dissolve in rain water to create rain the is acidic. Acid rain corrodes metals and rocks like limestone which can damage buildings and statues. Acid rain can also change the PH in soil or rivers, this can mean that some species can not survive in that area.
Monday, 15 April 2013
4.10 describe the stages in the nitrogen cycle, including the roles of nitrogen fixing bacteria, decomposers, nitrifying bacteria and denitrifying bacteria
Nitrogen fixing bacteria turn nitrogen from N2 into ammonia.
Decomposers break down dead animals, urea and egested materials which releases nitrogen into the soil as ammonia.
Nitrifying bacteria convert nitrates into nitrogen.
Denitrifying bacteria break down nitrates into nitrogen which is then released into the atmosphere.
Here is a diagram to help explain:
This animation is very helpful:
https://www.classzone.com/books/ml_science_share/vis_sim/em05_pg20_nitrogen/em05_pg20_nitrogen.swf
Decomposers break down dead animals, urea and egested materials which releases nitrogen into the soil as ammonia.
Nitrifying bacteria convert nitrates into nitrogen.
Denitrifying bacteria break down nitrates into nitrogen which is then released into the atmosphere.
Here is a diagram to help explain:
 |
| commons.wikimedia |
This animation is very helpful:
https://www.classzone.com/books/ml_science_share/vis_sim/em05_pg20_nitrogen/em05_pg20_nitrogen.swf
4.9 describe the stages in the carbon cycle, including respiration, photosynthesis, decomposition and combustion
Respiration is carried out by animals and plants to release energy from glucose, the equation is:
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O . This means carbon is produced.
Photosynthesis is what plants do to create glucose the equation is:
6 CO2 + 12 H2O → C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 6 H2O. This means carbon is used.
Decomposition is happens when an animal dies, it is then eaten by a decomposer which releases the carbon in it back into the atmosphere.
Combustion is burning, if something with carbon is burnt it will release it into the atmosphere, e.g. a tree, fossil fuel.
This is one of many useful diagrams:
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O . This means carbon is produced.
Photosynthesis is what plants do to create glucose the equation is:
6 CO2 + 12 H2O → C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 6 H2O. This means carbon is used.
Decomposition is happens when an animal dies, it is then eaten by a decomposer which releases the carbon in it back into the atmosphere.
Combustion is burning, if something with carbon is burnt it will release it into the atmosphere, e.g. a tree, fossil fuel.
This is one of many useful diagrams:
 |
| frankswebspace |
4.8 describe the stages in the water cycle, including evaporation, transpiration, condensation and precipitation
Evaporation is when water turns into steam due to being heated
Transpiration is when water is evaporated from leaves
Condensation is when water vapour turns into water due to being cooled, this forms clouds
Precipitation is when water is released from a cloud, e.g. rain, snow, hail
The best way to understand this is with a diagram:
Transpiration is when water is evaporated from leaves
Condensation is when water vapour turns into water due to being cooled, this forms clouds
Precipitation is when water is released from a cloud, e.g. rain, snow, hail
The best way to understand this is with a diagram:
 |
| cleanwatercampaign |
Saturday, 30 March 2013
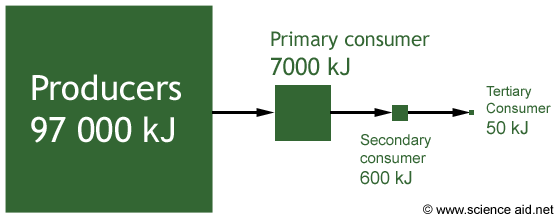
4.7 explain why only about 10% of energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next.
The reason why not all of the energy will make it to the next tropic level is that some of it will be used up on the level it is at. The energy is used for the life processes of the animal that it is in.
e.g If a bunny rabbit eats a cabbage, it will use some of the energy to keep warm, some to move e.c.t so fox only gets some of the original energy from the cabbage.
e.g If a bunny rabbit eats a cabbage, it will use some of the energy to keep warm, some to move e.c.t so fox only gets some of the original energy from the cabbage.
4.6 understand the transfer of substances and of energy along a food chain
As one thing consumes another the energy and other things inside it- for example fat and vitamins- get transferred to the consumer. If you eat a fatty piece of beef you get the fat from the cow.
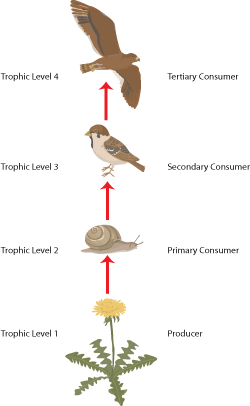
4.5 understand the concepts of food chains, food webs, pyramids of number, pyramids of biomass and pyramids of energy transfer
 |
| sciencebitz.com |
A food chain shows the transfer of energy up the food chain beginning with the producers then the primary consumers and so forth.
| king.portlandsschool.org |
A food web links several animals within a habitat showing what consumes what and is consumed by what.
 |
| BBC.co.uk |
 |
| BBC.co.uk |
 |
| scienceaid.net |
Saturday, 23 February 2013
4.4 explain the names given to different trophic levels to include producers, primary, secondary and tertiary consumers and decomposers
Different trophic levels= different feeding levels
Producer (turns light energy into chemical energy)
v
Primary consumer (eats the producer and gains its energy)
v
Secondary consumers
v
Tertiary consumers
When these organism die they are broken down by decomposers- fungi and bacteria.
Producer (turns light energy into chemical energy)
v
Primary consumer (eats the producer and gains its energy)
v
Secondary consumers
v
Tertiary consumers
When these organism die they are broken down by decomposers- fungi and bacteria.
4.3 explain how quadrats can be used to sample the distribution of organisms in their habitats.
A sample square is taken at random. The number of a population in that square is taken. This is repeated in different areas and compared to show where populations are dense and not.
4.2 explain how quadrats can be used to estimate the population size of an organism in two different areas
A square of around a meter takes a sample from a area and the populations are counted. This can be repeated many times before being multiplyed out as if it were the complete area of the land. Two different samples can be put in two separate areas and the sampling done for both will estimate population for both areas.
4.1 understand the terms population, community, habitat and ecosystem
Population
Number of individuals in a particular species.
Community
Populations of different species interacting.
Habitat
The area where a population lives.
Ecosystem
A community in a particular habitat made up of different populations interacting with in the habitat.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)